The purpose of a vehicle’s exhaust system is to move combustion gases out of the engine and through the catalytic converter (CAT) to remove harmful pollutants, at which point it can safely exit the tailpipe and disperse into the atmosphere, while also directing noise away from the passenger compartment.
However, exhaust systems should be sealed, so if there’s a leak, especially if it’s before the CAT, toxic fumes may seep into the vehicle’s cabin, a serious safety concern. What’s more, a leak can also impact engine performance and efficiency by disrupting the pressure balance in the exhaust system.
One of the main causes of exhaust leaks is a bad exhaust gasket. Gaskets serve as seals between the different components, allowing gases to flow through the entire system without escaping.
Thankfully, in this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about exhaust gaskets. We’ll start by exploring the different gasket types and their purposes. Then, we’ll explain how to choose the right exhaust gasket size for your vehicle, followed by detailed installation instructions.
Let’s get started.
Understanding the Purpose of Exhaust Gaskets
Exhaust Manifold Gasket
Nearly all internal combustion engines have exhaust manifold gaskets. These mechanical seals ensure a tight fit between the engine's cylinder head and the exhaust manifold, a juncture where hot exhaust gases pass through on their way out of the engine.
To withstand these intense temperatures, manifold gaskets are typically made from durable heat-resistant materials like multi-layer steel (MLS), graphite, ceramic composites, or a mix of these.
The number of exhaust manifold gaskets in a car depends on its engine design. While many vehicles have a single manifold gasket (such as with a 4-cylinder engine), V6 or V8 models have two.
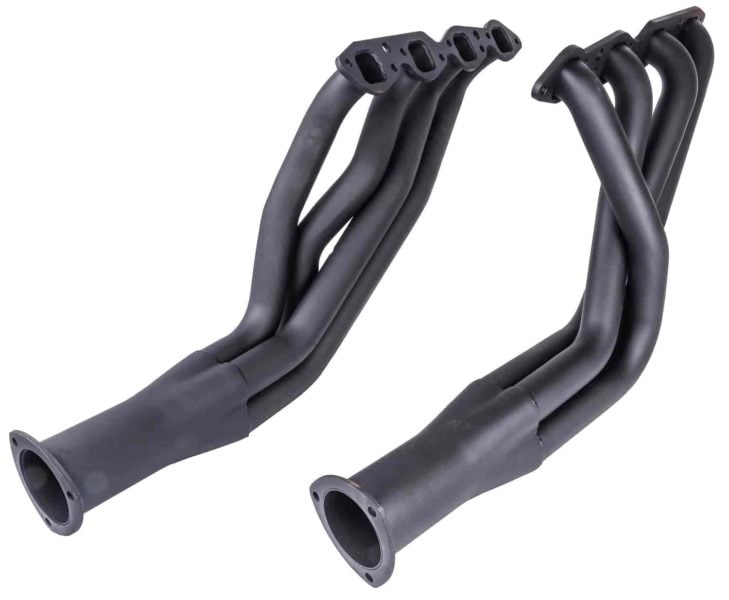
Header Gaskets
Header gaskets are a key component in vehicles equipped with aftermarket exhaust headers, which are designed for improved performance. These gaskets form a seal between the engine’s cylinder head and the exhaust headers, replacing the more restrictive exhaust manifolds, preventing leaks that can lessen engine efficiency and power.
Due to the added performance demands, exhaust header gaskets must endure even higher temperatures and pressure than manifold gaskets. For this reason, they are often made from materials like reinforced MLS, copper, or temperature-resistant composites.
A well-sealed header is needed for maximizing exhaust flow and engine output, making the durability and quality of header gaskets important for any performance-focused vehicle modification.
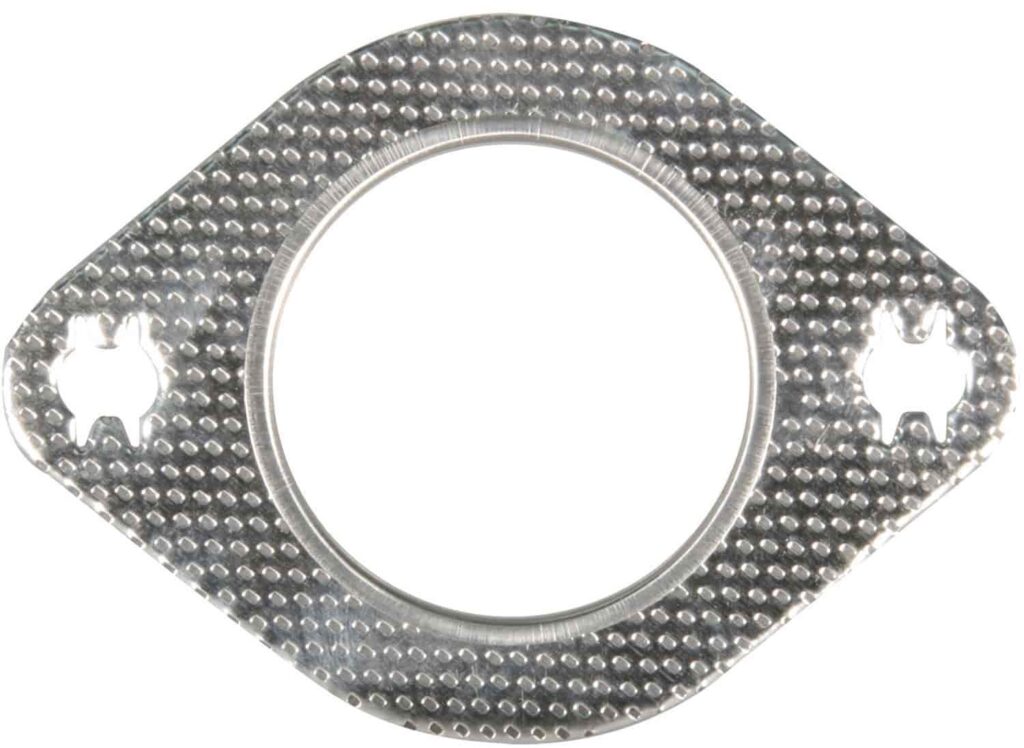
Exhaust Flange / Collector Gasket
Next up are exhaust flange or collector gaskets, which are usually located on the other side of the manifold or header gasket, at the joint where the exhaust pipe connects to other components, like the muffler, catalytic converter, or other pipe sections.
These gaskets are designed to accommodate the vibration and heat expansion typical in exhaust systems, ensuring a tight seal despite these conditions.
To account for the added movement, flange gaskets are often made from materials like high-temperature metals or composite fiber. Their shape and size vary depending on the vehicle's make and model, as they must match the flange's configuration precisely.
Pipe Gasket
The final exhaust gasket on our list is the pipe gasket, which seals the connections between different sections of the exhaust pipe so gases can flow through the system without any leaks.
Made from materials like metal, high-temperature or composite fibers, pipe gaskets are built to withstand the exhaust system's harsh conditions, including heat, pressure, and corrosive gases.
As with other gaskets, sizing is incredibly important to ensure a tight seal. The pipe gasket must match the dimensions of the pipes it connects, or else gas is likely to seep out.
Exhaust Gasket Sizing Explained
Factory/OEM Exhaust Systems
When replacing exhaust gaskets on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) exhaust systems, finding the right size is fairly simple.
The easiest way is to search by the year, make, and model of your vehicle. JEGS, for instance, offers a user-friendly interface where you can input these details to find the exact gasket for your vehicle's specifications.
This method ensures you get a gasket that matches the original design of your car's exhaust system, maintaining the manufacturer's intended performance and fit.
Custom Exhaust Systems
For custom-built cars with unique exhaust systems, you’ll need to take a few measurements.
First, remove the existing gasket and use a tape measure to measure its Inner Diameter (ID) and Outer Diameter (OD). These measurements ensure that the new gasket will align properly with the pipe openings.
Next, measure the bolt-hole spacing. If your exhaust flange is circular, you'd measure the bolt circle diameter, which is the distance from the center of one bolt hole to the center of the bolt hole directly across from it. If the gasket is a different shape, careful measurements will need to be made and confirmed to ensure you order and receive the correct part.
With these measurements collected, you can then look for a gasket that matches these specifications. If a pre-made gasket isn't available, these measurements are what you'd provide to a supplier for a custom gasket.
For your convenience, JEGS makes the process of finding aftermarket exhaust gaskets as simple as possible by allowing you to filter our gasket inventory by size, material, port style, type, width, height, and more.
Guide for Installing Exhaust Gaskets
Installing an exhaust gasket is an important task that requires precision and attention to detail. Whether you’re dealing with a factory or a custom exhaust system, the following steps will guide you through the installation process:
- Preparation: Before beginning, ensure the vehicle is safely supported and the engine is cool to the touch. Gather all necessary tools, including a socket set, wrenches, a torque wrench, and a wire brush or sandpaper.
- Removal of the Old Gasket: Carefully remove the component (exhaust manifold, header, pipe, or flange) to which the gasket is attached. Use a gasket scraper to remove any remnants of the old gasket material from both surfaces it was adhering to. It’s important that these surfaces are clean and smooth to ensure a proper seal.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Clean the surfaces where the new gasket will sit with a suitable solvent to remove dirt or oil. Inspect these surfaces for any damage or irregularities preventing a good seal.
- Gasket Alignment: Align the new gasket with the bolt holes and the contours of the surfaces. For manifold and header gaskets, make sure the port holes in the gasket align precisely with the exhaust ports on the engine and manifold/header.
- Installation: Place the gasket onto the surface and reattach the component. Hand-tighten the bolts in a crisscross pattern to ensure even pressure. Then, use a torque wrench to tighten the bolts to the manufacturer's recommended specifications. Be careful to avoid over-tightening, which can warp the flange or damage the gasket.
- Final Checks: After installation, start the engine and inspect for any signs of leaks. It’s not uncommon to need a slight retightening of the bolts after the engine reaches its operating temperature.
JEGS: For All Your Automotive Needs
And there you have it, the full rundown on exhaust system gaskets. For all your automotive needs, consider JEGS, a leading supplier of performance auto parts, including exhaust gaskets. Browse our full inventory today and have your order sent straight to your garage.
Still have questions? Contact our team today.