Automatic transmissions typically reach 150,000 miles without much issue; some even surpass 300,000 miles. However, if this vital component starts overheating, its longevity may be cut short.
There are many possible causes of overheating, including problems with your transmission cooler lines (also referred to as cooler hoses or transmission tubing). These help maintain safe temperatures by sending hot fluid from the transmission to a cooler and then back.
If your cooler lines start having issues, such as leaks, blockages, or wear and tear, it can impact the efficiency of the cooling process, leading to overheating.
Thankfully, JEGS is here with an in-depth transmission cooler hose guide covering everything you need to know to resolve any issues and get back on the road.
We'll start by reviewing how cooler lines work and the importance of transmission fluid. Then, we'll explore the different parts of this system. Finally, we’ll share how to choose the best hoses and securing hardware for your needs.
Let's get started.
Understanding Transmission Cooler Line Systems
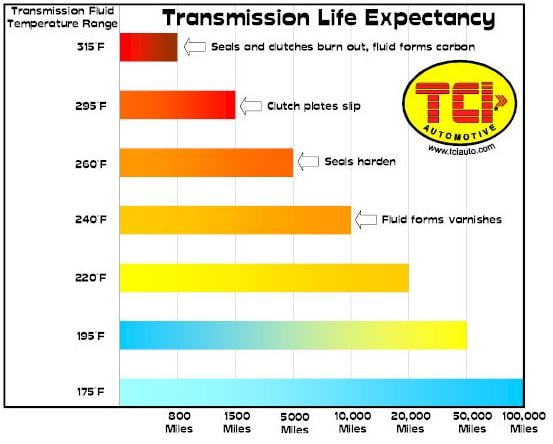
The cooling line system in an automatic transmission ensures temperatures stay within a safe operating range, typically between 175°F and 200°F.
This system works by circulating hot automatic transmission fluid (ATF) from the transmission to the radiator for cooling and then returning. The cooler lines consist of both "hot" and "cold" lines. The hot line carries the heated ATF to the radiator, while the cold line returns the cooled fluid back to the transmission.
Without this constant ATF flow, overheating may occur, typically at temperatures of 270°F or more. Overheating can cause issues like warped components, degraded fluid, and damaged seals, potentially leading to costly repairs or complete transmission failure.
The Role Of Transmission Fluid
Transmission fluid helps your automatic transmission run smoothly by acting as a lubricant for its moving parts, reducing friction and wear.
More importantly, ATF acts as a coolant, helping to regulate the temperature within the transmission system. As the vehicle operates, the transmission generates heat. This heat is absorbed by the transmission fluid, which is then circulated through the cooler lines to the radiator, where it is cooled and then returned to start anew.
Maintaining your ATF's quality and level is vital to prevent increased friction and overheating. Thankfully, regular fluid checks and changes (recommended every 30,000 to 60,000 miles in many cases) can help preserve the lubricating and cooling properties of your ATF.
Transmission Oil Cooler Line & Hose Components
Now that you have a better understanding of how this system works, let’s look closer at the various cooler line and hose components:
- Transmission Pump: This small pump (located within the transmission) circulates the ATF. It feeds the hydraulic system and pumps the fluid out of the transmission through the hot line of the cooler lines. The pump's role is crucial in maintaining the proper flow of fluid and ensuring efficient cooling.
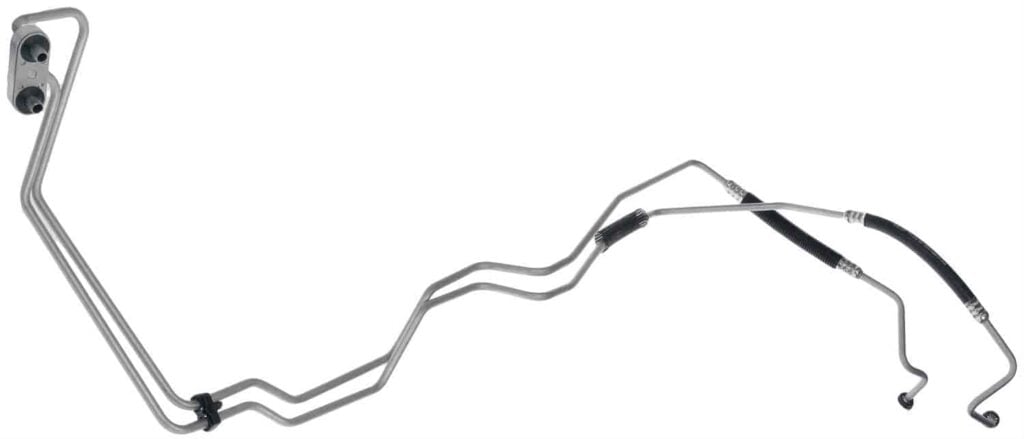
- Metal Lines: Metal cooler lines are typically pre-bent and come with fittings at each end. These are usually made of steel and designed for specific makes/models. Their design makes them durable, with a high resistance to heat and pressure, and allows for easy installation and a secure fit.
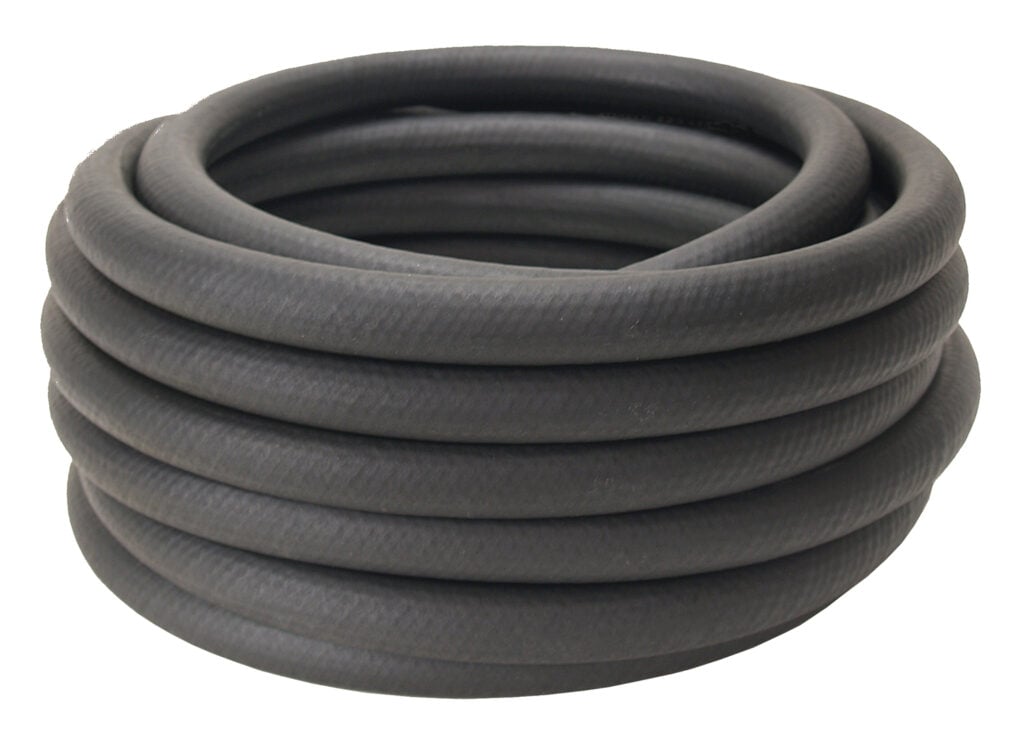
- Rubber Hoses: High-pressure rubber cooler lines specifically for transmission fluid are a popular choice due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. These hoses are known for their transmission fluid resistance, as well as their flexibility and wide bending radius, allowing for a simple install that doesn’t involve a wide assortment of fittings.
- PTFE Hoses: With their high chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) hoses make fantastic cooler lines. These hoses offer excellent durability compared to standard rubber options and are particularly well-suited for high-performance applications like off-roading or racing.
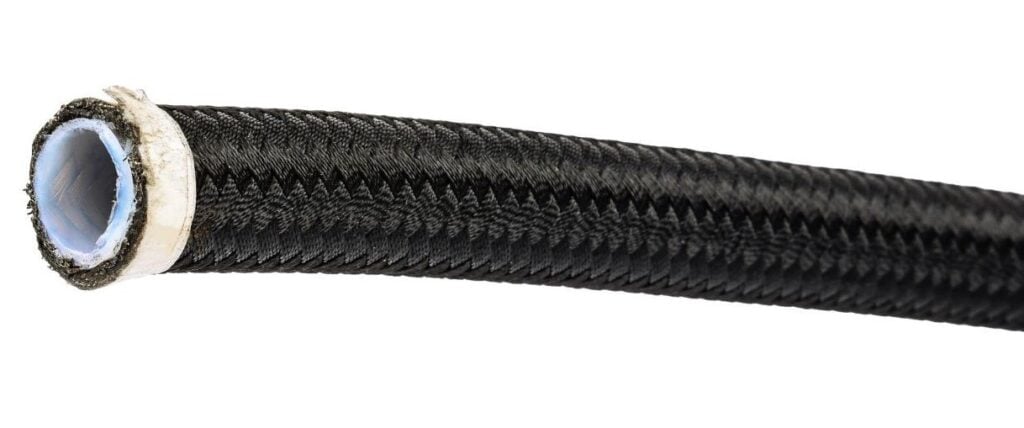
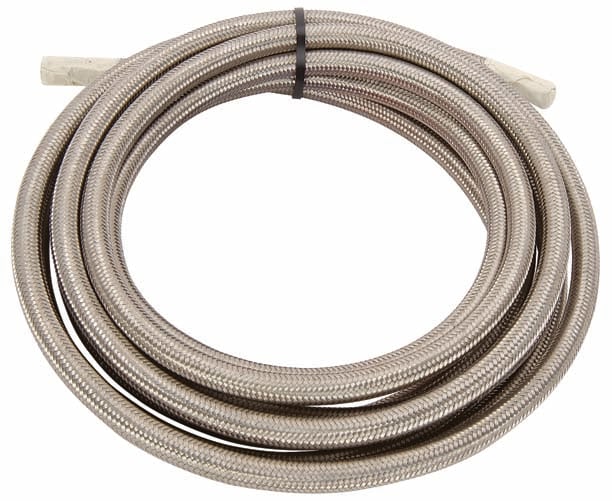
- Nylon Braided Lines: This type of transmission tubing provides better durability and reliability compared to rubber hoses. A nylon braided line is a rubber hose wrapped in a protective layer of nylon. They are not only versatile but offer improved resistance to abrasion and impact.
- Steel Braided Lines: These lines offer top-tier durability, impact resistance, and abrasion protection. Designed to handle high temperatures and pressures, these are ideal for harsh conditions. The steel mesh reinforcement prevents expansion, ensuring consistent performance in high-performance scenarios like racing.
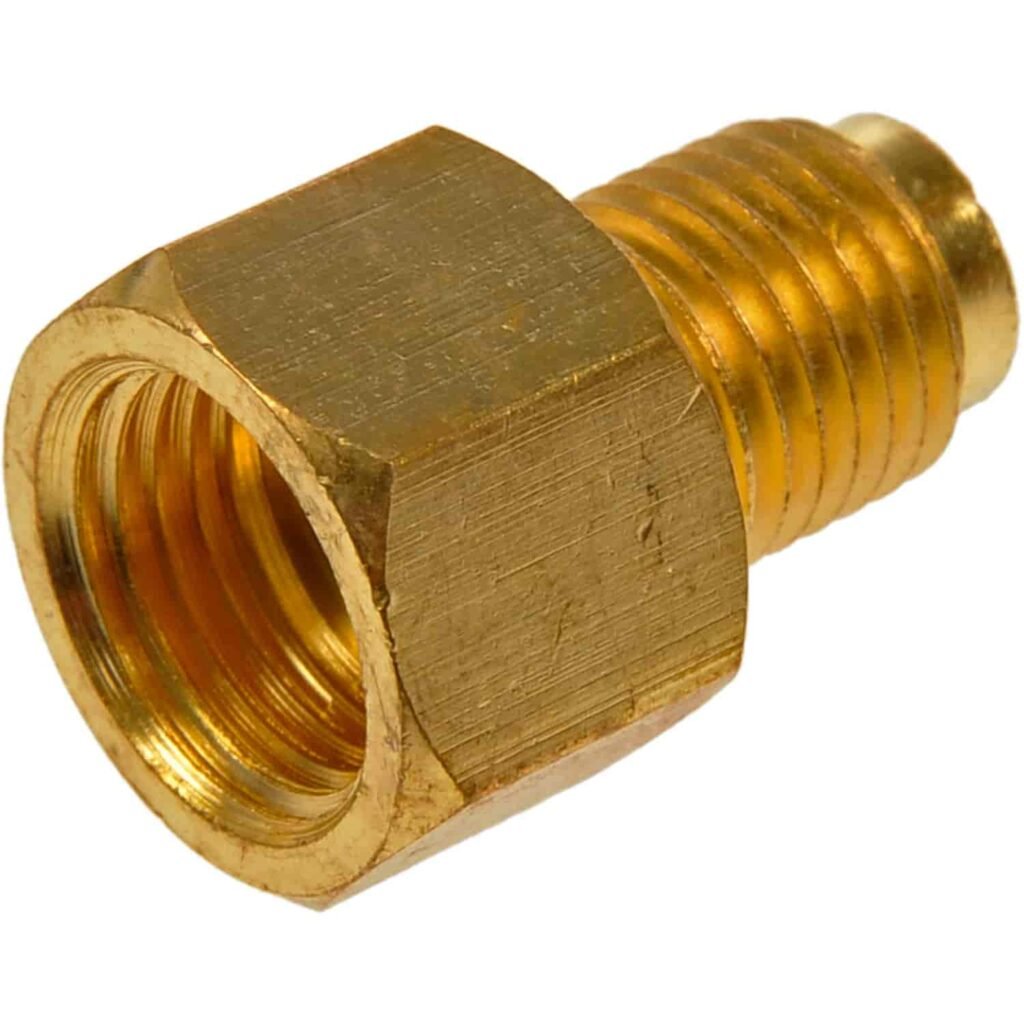
- Standard Fittings: Standard fittings, often found on transmissions and radiators, are tailored to specific vehicle models. They typically are threaded to securely hold metal cooler lines in place, ensuring a leak-proof connection and maintaining fluid flow integrity within the cooling system.
- Barb Fittings: These fittings make installation a breeze. Just push the barbed end into the hose, and tighten with a high-pressure clamp, and viola, a secure connection. Barb fittings are also cost-effective and come in various sizes. They are ideal for installing an aftermarket transmission cooler or connecting rubber lines together.
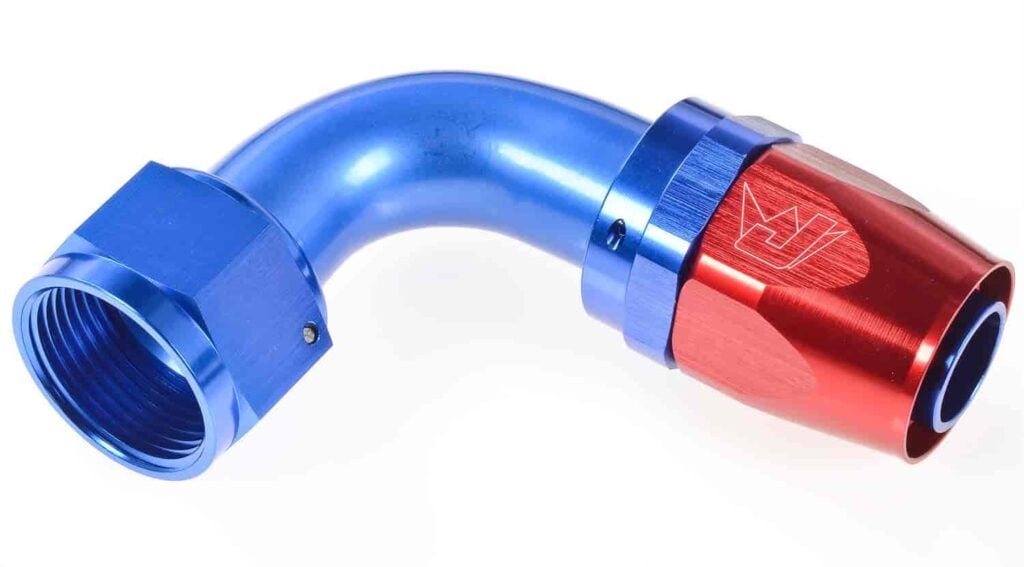
- AN Fittings: AN (Army-Navy) aluminum fittings cost more than barb fittings but provide a more secure connection. They are popular in high-performance applications, such as racing or off-roading, where reliable, robust connections are key. AN fittings are versatile and come in various sizes and angles to meet different installation needs.
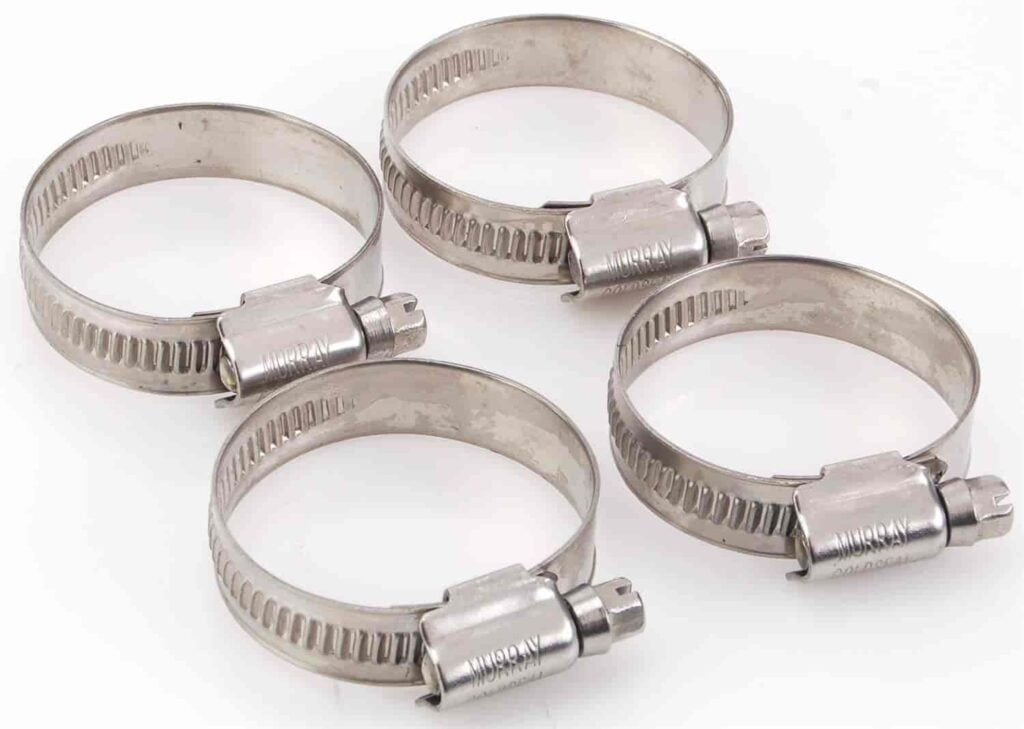
- Hose Clamps: Hose clamps are essential for securing the cooler lines and preventing leaks. Several types are available, each with its advantages and recommended uses. Worm clamps are the most common and cost-effective option for rubber transmission lines. They provide a secure grip and are easy to adjust and remove.
What To Use With Transmission Cooler Lines: Choosing the Right Car Plumbing Components
When selecting the right hose for your transmission cooler lines, consider the type of transmission, the transmission cooling line configuration, and your vehicle's specific requirements.
For vehicles with pre-bent metal lines, OEM replacement lines are recommended for a proper fit and optimal performance. These are vehicle-specific, ensuring easy installation and reliable operation.
Rubber lines are a cost-effective choice for temporary fixes or custom installations but should be kept away from hot components like exhaust systems and engine parts to prevent damage.
Braided lines, such as nylon or stainless steel, are suited for performance applications like towing a heavy load or enjoying a day at the track, offering enhanced durability and abrasion resistance.
For high-performance vehicles, you can also consider AN fittings coupled with PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) hoses, which offer superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance.
When using AN fittings, ensure the correct adapter is used, especially with aluminum transmission cases, to avoid the risk of splitting due to improper fitting.
Select the right hose based on factors like durability, heat resistance, flexibility, and cost, and ensure you choose appropriate fittings and clamps for a secure, leak-free connection.
JEGS: For All Your Automotive Needs
Whether you need OEM replacement lines, rubber hoses for temporary fixes or custom projects, or braided or PTFE lines for performance applications, JEGS has you covered.
With a wide range of transmission cooler lines, fittings, and hose clamps, JEGS provides high-quality products to meet your automotive needs.
Still have questions? Contact our team today.