Often, automotive maintenance items aren't replaced until a problem surfaces. One such component is the spark plugs wires. These parts transfer voltage from the ignition distributor or coil to the spark plug where fuel and air is ignited in the combustion chamber of the engine. When the condition of spark plug wires degrades, the voltage reduces or stops completely, causing drivability symptoms. Sometimes it's easy to spot damaged spark plug wires and sometimes more investigation is required in addition to a visual inspection. But how do you tell if the symptoms your engine is giving are due to spark plug wire problems? Read on to find out more.
Examples Of Physical Damage
When inspecting spark plug ignition wires for physical damage, look for anything that is more than light or minor imperfections to the surface of the wires. Check the boots to ensure they don't show signs of burning or melting from being near the exhaust manifold or header. Look for any cracking or degradation on both the boot and wire outer covering. Also carefully remove the boot from the spark plug and distributor or coil and look inside. If there is any corrosion on the terminals, the wire should be replaced. Although the connector can be cleaned, most likely the corrosion will come back in a short time. Another observation that can be done is to turn on the engine and open the hood at night outside. Then carefully (without touching anything hot or moving like exhaust or belts) look for sparks jumping from the spark plug wires and ends to other parts. There should be no sparks seen with a properly running ignition system.
Engine Is Idling Rough
A damaged spark plug wire may produce a rough idle from the engine. This is due to incomplete combustion and fuel burn at low rpm due to low or no voltage reaching the spark plug. This buildup of ab incomplete burn of fuel causes inconsistent combustion, resulting in the rough sound heard at idle.
Engine Hesitation
Damaged spark plug wires can also cause engine hesitation. Symptoms of engine hesitation include bogging, stumbling, low power, or misfiring during acceleration. As with rough idling symptoms, the incomplete ignition of fuel and air in the combustion chamber causes the loss of power that leads to hesitation.
Visible Damage To The Spark Plugs
When spark plug wires are not working properly, reduced or no voltage is received at the spark plug. Without enough voltage to produce the proper spark, the spark plug begins to accumulate raw fuel and other sediment, making ignition more difficult to accomplish. This can be confirmed by a darkening of the insulator (usually white) and tip, electrode ("hook"), and the top of plug threads. The solution is to either replace or clean the spark plug to restore functionality.

Engine Is Misfiring
Spark plug wires that are damaged or defective can lead to engine misfires in addition to the aforementioned other symptoms. This condition produces backfiring, popping, and banging, along with a jerking of the vehicle upon acceleration. The inconsistent burning of fuel and air in the engine cylinders produces this behavior.
Testing Spark Plug Wires
One way to determine if a spark plug wire is working properly or not is by testing its resistance with a digital multimeter. To begin testing, select the correct ohm reading on the multimeter (some have an auto function that finds and displays the correct measurement). Then use the positive probe on one end of the wire and the negative probe on the other. The displayed result is the number of ohms of resistance the wire has. This will change depending on the length, so a good way to create a baseline ohm reading is to divide the number of ohms by the length of the spark plug wires. For example, a spark plug wire about 2 feet in length with 3,000 ohms shown on the multimeter means it has 1,500 ohms of resistance per foot. If you are able to determine the ohm range of a properly functioning spark plug wire from the manufacturer or vehicle shop manual with OEM wires, you can compare to the reading and if too many ohms is observed, the spark plug wire is defective and in need of replacement. However, if you don't know what the resistance range should be for your wires, you will need to do a comparison of the other spark plug wires on your engine. Ideally, if you get a consistent ohm reading per foot on 3 or more wires, and then find a wire with more resistance per foot, this would indicate a possible bad component. Another test that can be done is by bending the wire gently in different places such as where the boot connects to the wire while having the multimeter probes connected. Notice any changes in ohms with bending and if there are significant change, the wire should be replaced.

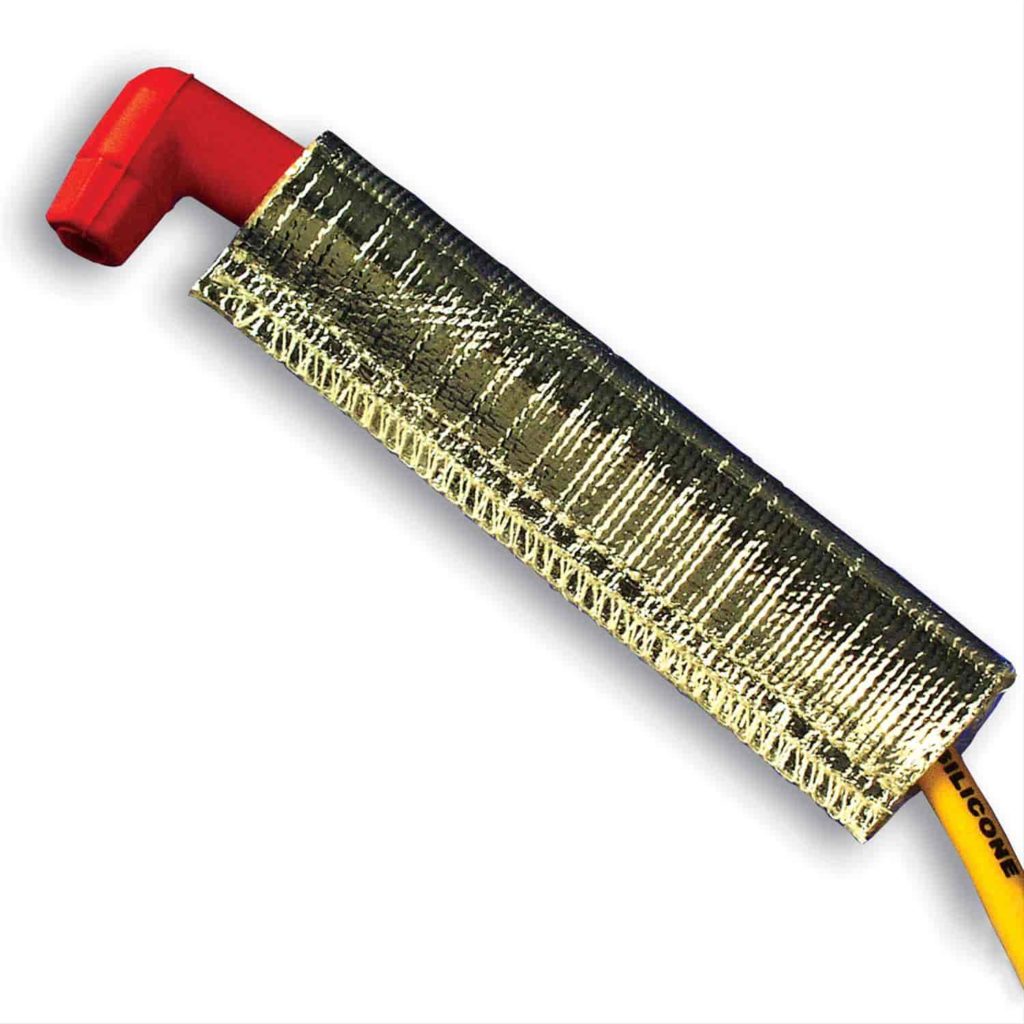
How To Protect Spark Plug Wires From Damage
There are several ways to protect spark plug wires from damage. The first is to keep them away from heat sources like the headers and manifolds as well as direct contact with the engine block. This can often be helped with the use of spark plug wire looms and separators, which secure the wires away from high-heat sources and keep them from moving. Another option is spark plug wire boot guards and heat sleeves. These tubes slide over the spark plug boots, insulating them from heat that would cause melting and burning.