Transmission coolers play an important role in preventing failure and overheating. Whether you have a high-performance vehicle or frequently tow heavy loads, a transmission cooler is a critical component in ensuring the longevity and reliability of your vehicle's transmission. In this article, we'll discuss the different types of transmission coolers available and how to choose the right size and temperature for your specific needs.
What Does a Transmission Cooler Do?
A transmission cooler either built into the radiator ("radiator transmission cooler") or typically mounted in front of it is designed to cool the transmission fluid. The transmission fluid is responsible for lubricating and cooling the transmission components, and when it overheats, it can cause damage. The transmission cooler also helps maintain a consistent temperature by dissipating the heat generated by the transmission fluid as it flows through the cooler.
What is the Ideal Transmission Temperature?
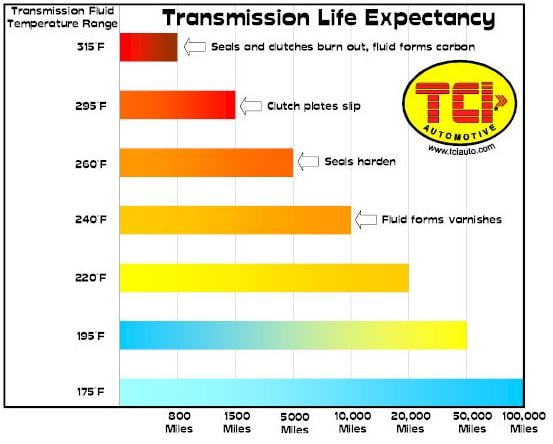
The ideal transmission temperature is between 160°F and 200°F. Any higher than that, and the fluid can start to break down and cause damage to the transmission. However, in extreme situations like towing heavy loads or racing, the temperature can exceed the ideal range. This is where a transmission cooler comes in handy as it can help reduce the temperature and prevent damage to the transmission. Below is a very helpful transmission fluid temperature chart from TCI Automotive showing the effects of transmission fluid temperature on transmission components.
Types of Transmission Coolers
There are three main types of transmission coolers: stacked plate, tube and fin, and plate and fin. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best transmission cooler for you will depend on your specific needs.
Stacked Plate Transmission Cooler
Stacked plate transmission coolers are the most efficient and effective type of cooler. They have a series of plates stacked on top of each other, and the transmission fluid flows through the small passages between the plates. This design provides a large surface area for the heat to dissipate, making it very efficient. They are also very durable and can handle high flow rates.

Tube and Fin Transmission Cooler

Tube and fin transmission coolers are the most common type of cooler. They have a series of tubes with fins attached, and the transmission fluid flows through the tubes while the fins dissipate the heat. They are less expensive than stacked plate coolers but are not as efficient.
Plate and Fin Transmission Cooler
Plate and fin transmission coolers are similar to tube and fin coolers, but they have plates instead of tubes. The plates have small fins on them, and the transmission fluid flows through the passages between the plates. They are more efficient than tube and fin coolers but not as efficient as stacked plate coolers.

Choosing a Cooler Size
Choosing the right size of transmission cooler is important to ensure that it can handle the amount of heat generated by your transmission. The general rule of thumb is to choose a cooler that is rated for at least three times the weight of your vehicle or the weight of the trailer you are towing. You should also consider the type of transmission you have and the amount of driving you do.
A transmission cooler is a critical component in maintaining the longevity and reliability of your vehicle's transmission. Choosing the best transmission cooler for your specific needs will depend on the type of driving you do and the weight of your vehicle or trailer. Stacked plate coolers are the most efficient, but tube and fin and plate and fin coolers are also effective and less expensive. Always ensure that the cooler you choose is rated for at least three times the weight of your vehicle or trailer and can handle the amount of heat generated by your transmission.